What is microbial biomass, and why is it interesting for foods and ingredient suppliers?

Anita Hartog (AH): “The expression ‘microbe’ is utilised here in the wide connotation of microorganisms, fungi, yeast and algae. Microbial biomass is the consequence of the fermentation, by these microbes, of organic substrates such as by-products from the sugar business and other foodstuff processing residues, or hydrogen substrates which includes methanol and methane. Biomass ideal for human or animal consumption has usually been referred to as one mobile protein (SCP).
“Utilizing these types of edible microorganisms isn’t a completely new strategy throughout Planet War I, for example, Germany generated edible yeast for foods on a substantial scale. But the strategy of working with microbial biomass as a food items resource actually started attaining steam in the 1960s, sooner or later ensuing, for example, in the 1980s start of mycoprotein (Quorn), derived from the Fusarium venenatum fungus.
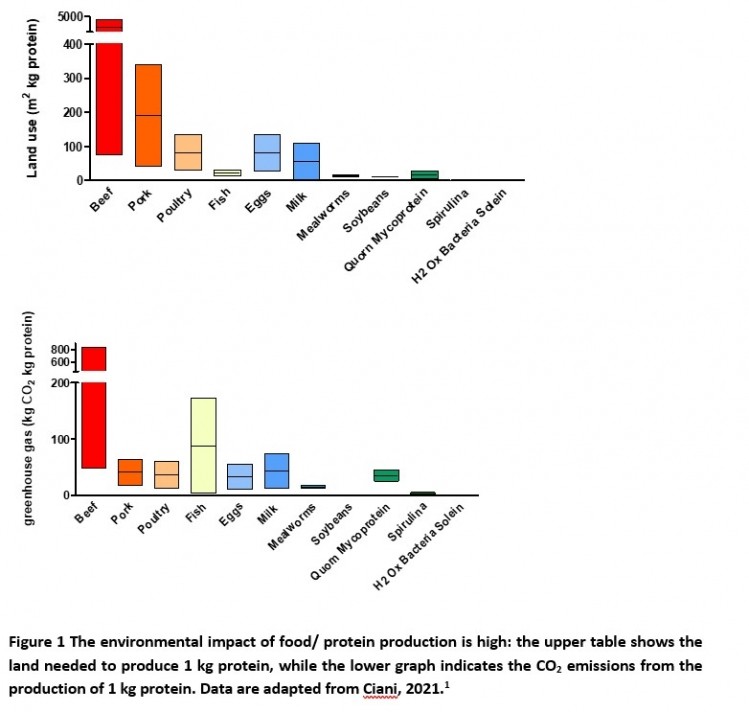
“The most important incentive for utilizing microbial biomass to generate foods has been its sustainability: it does not involve as much arable land or h2o as boosting animals and crops. And it can change facet streams or even discarded substrates into protein, minimizing wastage. But microbial biomass can offer customers and producers a great deal much more.
Is microbial biomass protein as high in protein as meat and dairy?
AH: “The protein content of algae, these as spirulina, can be as substantial as 46-65% of its dry excess weight. Fungi can run to 30-50% protein: mycoprotein, for case in point, is 45% protein by dry fat. Microorganisms can be 50-80% protein. And yeast can have a protein material of close to 50% protein by dry bodyweight.
“These amounts assess perfectly to meat and dairy, and are even greater than a lot of plant-centered solutions.
“Even so, protein amount is not the total tale: you have to think about its quality and bioavailability as perfectly. Can the protein be applied by the human entire body?”
How do you figure out the high-quality of microbial biomass protein?
AH: “To do this, you will need to glimpse at the amino acid composition and digestibility of the proteins. Amino acids are important for advancement, tissue repair, and several other functions. As a benchmark, animal protein has all 9 crucial amino acids.
“The amino acid profiles for microbial proteins in point assess pretty very well with meat and fish, and with the conventional requirements for human usage as described by the FAO/WHO. Plant proteins, on the other hand, commonly lack or are minimal in some of these crucial amino acids.
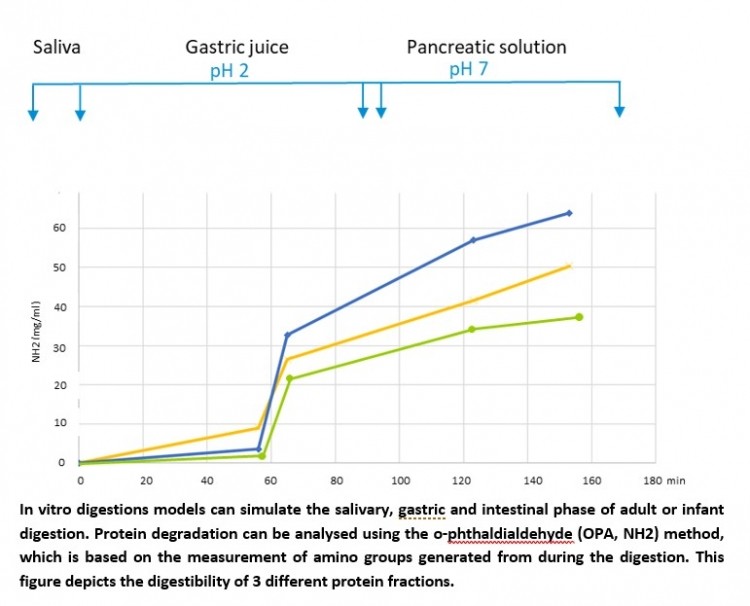
“But these amino acids also will need to be ‘available’ for the physique to use: this is the place digestibility arrives in. Digestion starts off in the mouth, with mastication and saliva, and continues in the belly (with the gastric juices) and the intestines (with bile, pancreatic juice and intestinal juice).
“Different proteins and protein fractions will be degraded at unique prices all through the numerous digestive phases, as the amino acid chains are broken down into particular person amino acids. The latter can be absorbed in the compact intestine, and released into the blood stream, which provides them in the course of the physique.
“The digestibility of microbial biomass proteins may differ. Fungi, for illustration, have a digestibility very similar to eggs and milk, while algae is a lot less digestible. By breaking down the algae’s mobile walls, its digestibility can be improved.”
What other nutritional benefit or well being benefits can microbial biomasses supply?
AH: “Edible microbial biomasses can be fantastic vegan sources of a selection of nutritional vitamins, fat, fibres, and so forth. For example, K2 vitamins, which are generally not located in crops, can be produced by particular microbes. K2 performs a job in blood clotting, bone health and coronary heart health and fitness.
“Algae, on the other hand, can be a great resource of the omega 3 fatty acids EPA and DHA. These are extremely essential for the structure of the body’s cell walls, and can influence the heart, lungs, blood vessels and immune system. Omega 3 fatty acids like EPA and DHA are most generally furnished by fish, so it is really exciting to have a vegan supply.
“The fibres from the microbial biomass can also present more overall health benefits. In this context, yeast and algae can be resources of beta glucans, which have been revealed to effect immune features.
References:
1. Ciani M, Lippolis A, Fava F, Rodolfi L, Niccolai A, Tredici MR: Microbes: Food for the Future. Foods 2021, 10.

